|
The Evolutionary Theory of
Sex:
The
Evolutionary Role of Cancer
 The wider the population variation, the safer it is, because
it can determine changes of environment earlier. At the same
time, the selection is higher and the population has to pay
high cost for its evolution. On the contrary, if the
variation is narrow, the evolution is less costly, but the
risk is higher. So, in every environment a certain optimum
of variation exists that minimizes both the risk and the
cost of evolution.
The wider the population variation, the safer it is, because
it can determine changes of environment earlier. At the same
time, the selection is higher and the population has to pay
high cost for its evolution. On the contrary, if the
variation is narrow, the evolution is less costly, but the
risk is higher. So, in every environment a certain optimum
of variation exists that minimizes both the risk and the
cost of evolution.
Entropy forces of environment (outbreeding, mutations,
errors of translation, radiation and heat) increase
variation. Natural selection narrows variation and therefore
regulates its optimum. But it works too coarse. For example,
the first to die from hunger will be children, the most
valuable, but weakest age group.
To prevent this, more precise mechanism was developed. This
mechanism is cancer.
Cancer is considered as
one of the mechanisms of natural selection, eliminating
individuals of a population according to their biological
value — sex, age and information role. Certainly, natural
selection uses all illnesses, but cancer is a tool specially
created for it. It precisely discharges children with birth
defects, as well as mature individuals not serving the tasks
of their age group.
The concept can explain
many features of cancer: its antiquity, generality, and
close relation with sex (Male > Female) and age (increases).
It can explain why children have high frequency of cancer of
relatively young connective tissue (blood and bones in
particular) while adults — cancer of more ancient epithelial
tissue which
lines both the
outside (skin) and the inside cavities.
It can also explain why the same type of cancer can be
caused by different reasons and, on the contrary, that one
factor can cause different forms of cancer.
Cancer
and age
Cancer may affect people at all ages,
even fetuses, but risk for the more common varieties tends
to increase with age.[1]
There exists a specific regulation of the age groups having
different biological value: children> reproductive age> an
active old age> a passive old age.
Cancer at children
Spectrum of
children cancer considerably differs from that of adults.
Adults have about 90 % of epithelial tissue cancers, while
children — only 0.8-2 %. The cancer of children is often
combined with various developmental anomalies, therefore it
is possible to consider, that it prevents anomalies of
growth and development from spreading. Thus, Wilms' tumor
(kidneys) happens at developmental anomalies of urinary
system, lymphomas — at hereditary agammaglobulinemia, a
cancer of bones at anomalies of osteogenesis, leucosis — at
Down syndrome.
Reproductive age
The main mission of reproductive age is to leave
offspring. Therefore the
cancer of reproductive age should eliminate those who do not
fulfill its purpose. Therefore, the long periods of
abstention and refusal of breastfeeding should raise risk of
a cancer.
According to new general concept of sex hormones the surplus
of the hormones has “carcinogenic” action, while hormones of
an opposite sex act as “anticarcinogens”. This view provides
an explanation why testosterone (poison for spermatozoids) is
present in sperm. The concentration of testosterone in man’s
blood after sex drops approximately 20 times []. It can be
assumed that without condoms his partner will get the
hormone.
Usage of condoms prevents pregnancy and sexually transmitted
diseases. At the same time the risk of developing breast
cancer increases tenfold. Medical statistics of
19th
century confirms this.
In Japan and Asian republics of Russia rate of breast cancer
was 10 times less compare to US and developed European
countries [].
Post reproductive age
The main mission of post reproductive age is to transfer
the cultural information to the descendants. Regulation in
this age group can also be carried out through a cancer,
instead of other illness. It’s well known that active
lifestyle prevents many diseases, including cancer. In
special studies, rats infected by an experimental cancer
were divided into two groups. One of them twisted the
squirrel wheel and has remained alive, while the control
group, without physical activity, perished.
Sexual dimorphism and cancer
The analysis made by P. M. Raevski and A. L. Sherman (1976)
for the malignant tumors, has shown, that phylogenetically
younger organs or systems of organs have higher values of
sexual dimorphism (higher incidence of tumors in males)
compare to old ones. For example, such phylogenetically
young formations as lungs, larynx, tong and esophagus had
the greatest sexual dimorphism values. On the contrary,
negative sexual dimorphism values were characteristic for
the reproductive system and thyroid glands.
Organs and tissues that are in contact with environment have
higher values of sexual dimorphism. Based on phylogenetic
rule of sexual dimorphism authors have predicted, that
lung cancer incidents will grow, while stomach cancer will
decrease, because the sexual dimorphism is increasing in the
first case, and decreasing in the second.
Opposite (mirrored) types of cancer
It was noted that an overdose of estrogen treatment of a
prostate cancer in men leads to its disappearance but at the
same time breast cancer develops (effect of mirror symmetry
of Gaussian curve). This tells us that deviation of hormonal
ratio from norm can lead to cancer. Similar picture exists
in breast and endometrial cancer statistics—those two forms
are discordant over time (Data of National Cancer Institute
for the years 1937, 1947
и
1969).
Another observation. In the US 87 million women were treated
by estrogens from osteoporosis. Analysis of the results
showed that the probability of such patients to develop
breast cancer was 1.44 times higher than average.
Treatment of cancer
Such understanding combined with the concept of
"fractional" sex leads to an important conclusion —
breast and prostate cancers are not always possible to treat
by hormones based on a passport sex. The fact is that sperm
androgens act as a “carcinogen”
for men and a preventive therapy of breast cancer for women.
If the goal of cancer hormone therapy is to bring the
extreme groups in each sex to their norm (middle of the
distribution) then it is necessary to administer different
hormones (one side of the curve should get androgens and
another — estrogens).
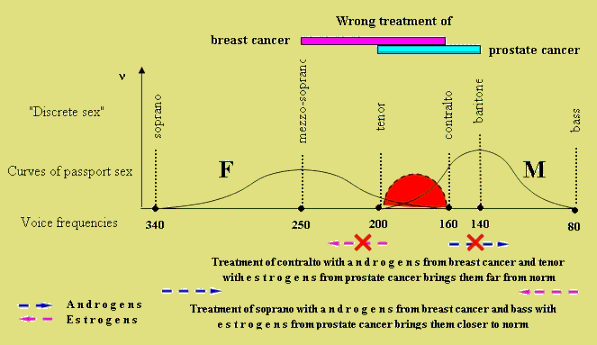
Figure. Breast and
prostate cancers should be treated based on “fractional”
sex.
Abscissa: Frequencies of
women and men voices (Hz).
Ordinate: Frequencies of phenotypes in population (ν).
Dashed red area – transgression zone. Colored lines – zones
of wrong cancer treatment.
In 2006 about 600 thousand women and 300 thousand men died
from breast and prostate cancer. They were treated by the
hormones of opposite sex. Some of them could have been saved
by using more selective therapy based on the person’s
hormonal status.
◄ Sexual Dimorphism in
Pathology ◄
Hormonal Sex
◄
Application of
“Teratological rule of sexual dimorphism” to the congenital
anomalies of the heart
References:
The evolutionary role of cancer.
The concept of negentropy. Geodakian V. A. (2006)
Intern. Conf. “Genetika v Rossii I Mire” (Genetics in Russia
and the World) Moscow June 28 – July 2 p. 45 (242)
Translated from Russian.
[1] Cancer Research UK
(January 2007).
UK cancer incidence statistics by age
[2]
Раевский П. М.,
Шерман А. Л. Значение пола в эпидемиологии злокачественных
опухолей (системно-эволюционный
подход). В
сб.: Математическая обработка медико-бнологической
информации. М., Наука, 1976, с. 170–181
|